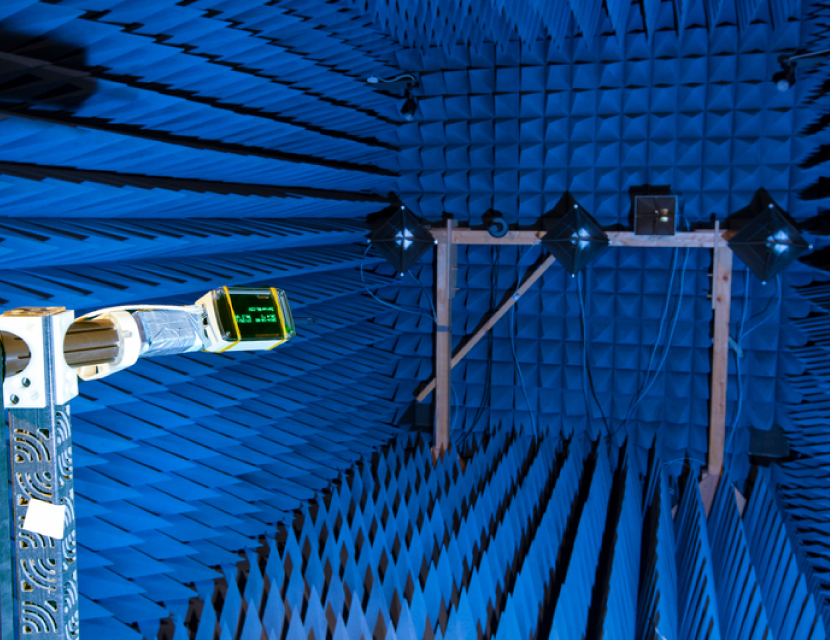
Radio Frequency (RF) Testing
Ensure optimal performance for electronic devices operating in wireless communication systems

WHAT IS RADIO
FREQUENCY TESTING?
Radio testing for electronics refers to the evaluation and assessment of the radio frequency (RF) performance of electronic devices or systems. It involves testing the ability of electronics to transmit and receive radio signals accurately and efficiently. This type of testing examines various aspects, such as signal strength, signal quality, frequency range, modulation techniques, interference resistance, and compliance with regulatory standards.


WHY IS RADIO
FREQUENCY TESTING IMPORTANT?
Radio testing ensures that electronic devices or systems meet the required specifications and perform reliably in wireless communication applications, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and other RF-based technologies.
RADIO FREQUENCY
TESTING TYPES
Several types of RF tests can be conducted for electronics to evaluate their RF performance. These tests include:
Transmitter Tests
Assess the performance of the device’s RF transmitter, including output power, frequency accuracy, modulation quality, and spurious emissions.
Spurious Emission Tests
Verify that the device does not emit unintended or harmful signals outside of its allocated frequency range, which could cause interference to other devices.
Radiated and Conducted Emission Tests
Determine the level of electromagnetic emissions from the device, both radiated (through the air) and conducted (through power and signal cables), to ensure compliance with regulatory limits.
Receiver Tests
Evaluate the ability of the device’s RF receiver to accurately receive and process signals, measuring parameters such as sensitivity, selectivity, and adjacent channel rejection.
Antenna Tests
Focus on the characteristics of the device’s antenna, including antenna gain, radiation pattern, impedance matching, and efficiency.
Receiver Blocking and Desensitization Tests
Assess the device’s ability to withstand strong adjacent signals without degradation or interference.
Frequency Range and Channel Occupancy Tests
Ensure that the device operates within the designated frequency range and adheres to the allocated channel occupancy requirements.
Modulation Accuracy Tests
Measure the accuracy and fidelity of the device’s modulation schemes, such as amplitude modulation (AM), frequency modulation (FM), or phase modulation (PM).
RADIO FREQUENCY
TESTING at TRS
TRS Test L abs have high-performance test equipment, such as an Agilent EXG (Vector Signal Generator), EXA (Signal Analyzer), and Rohde & Schwarz CMW-Z10 (Shielding Box).
TRS performs verification testing of a large range of both simple and complex modulated RF signal standards, such as GSM, Wi-Fi, BT, ZWave, and many other standards.
The setup allows our labs to respond rapidly to challenges and changed requirements during the development of a complex product. This enables the designer to optimize the design according to standards and beyond.
All tests are documented using a detailed, professional report structure that supports the chosen design solution.